Actinomycosis: Symptoms, Causes & Treatment - What You Need To Know
Is a hidden threat lurking within you, silently wreaking havoc, and often misdiagnosed? Actinomycosis, a rare but potentially devastating bacterial infection, often flies under the radar, mimicking other, more common ailments, making early detection a critical battle in the war for your health.
Actinomycosis, in essence, is a chronic bacterial infection caused by bacteria belonging to the Actinomyces genus. While various species can be responsible, Actinomyces israelii is most commonly implicated. These bacteria, often residing harmlessly on mucosal surfaces like those in the mouth and throat, become problematic when they breach the body's natural defenses. This breach can occur through several avenues: surgical procedures, trauma, or even poor dental hygiene, disrupting the mucosal barrier and allowing the bacteria access to deeper tissues. Once established, these infections can be challenging to treat, often requiring prolonged courses of antibiotics and, in some cases, surgical intervention.
The insidious nature of actinomycosis stems from its ability to mimic other conditions. The duration of symptoms can be anything from weeks to months before the patient seeks medical attention. The symptoms of actinomycosis are varied and depend significantly on the location of the infection within the body. The infection may affect different part of body like face and neck, chest and abdomen and even the pelvic region.
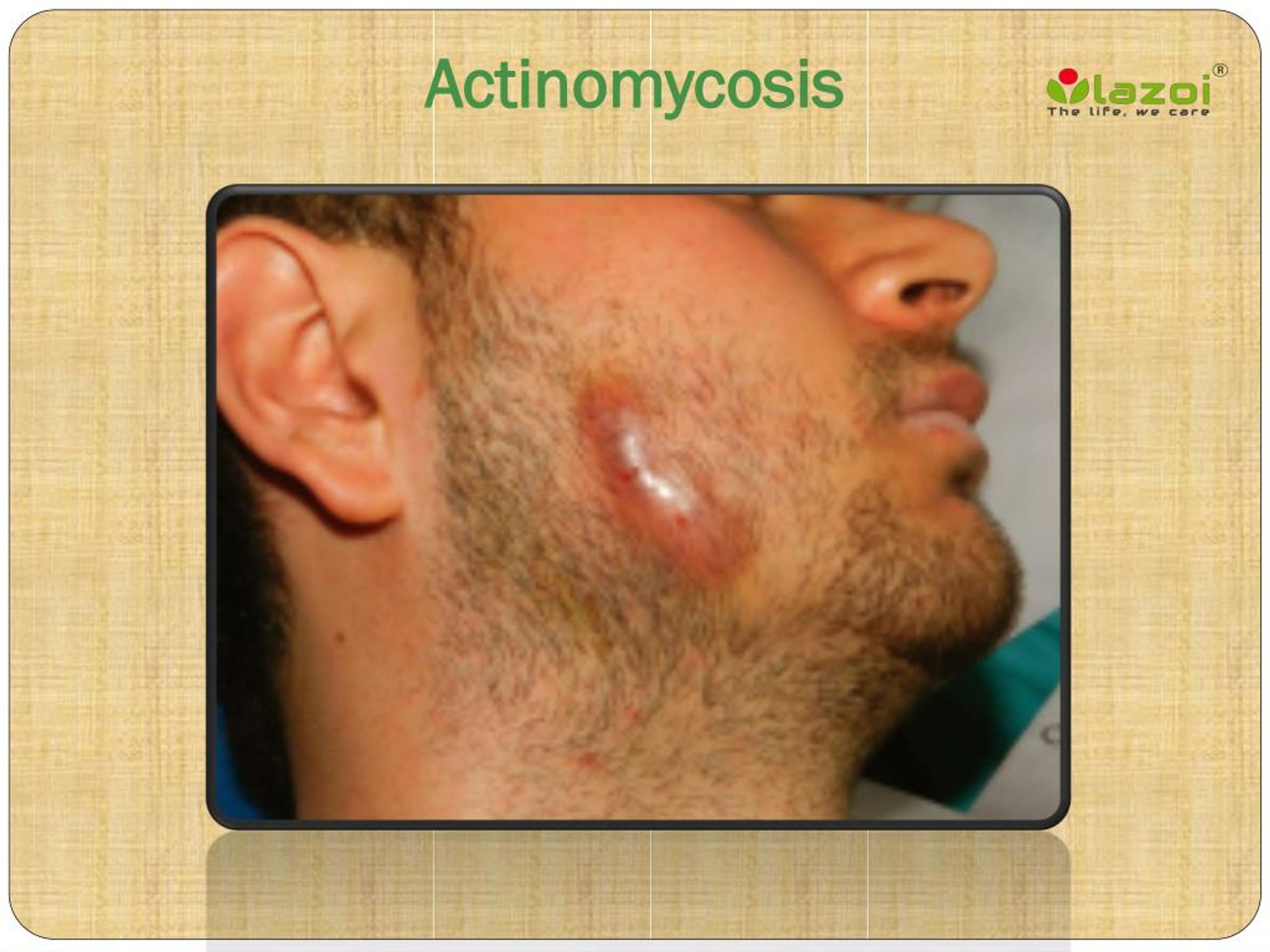
The symptoms of actinomycosis depend on the actual form of the disease.This condition is also known as a lumpy jaw;In a lot of cases, this form is not accompanied by pain;Pain might arise along with the inflammation of the soft tissues from the submandibular or peri
The main niche of Actinomyces is the oral cavity and pharynx. However, these bacteria can also be found in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, specifically the distal esophagus, and the genitourinary (GU) tract. The infection has no respect for anatomical barriers and can advance through different tissue planes.
| Characteristic | Details |
|---|---|
| Disease Name | Actinomycosis |
| Type of Infection | Bacterial |
| Causative Agent | Primarily Actinomyces israelii |
| Infection Sites | Oral cavity, face, neck, chest, abdomen, pelvis |
| Common Symptoms | Abscesses, draining sinuses, fibrosis, "lumpy jaw" (cervicofacial actinomycosis), chest pain (thoracic actinomycosis), abdominal pain (abdominal actinomycosis) |
| Diagnostic Methods | Clinical presentation, culture of pus or tissue, microscopic examination, imaging studies (CT scan, MRI) |
| Treatment | Prolonged antibiotic therapy (often penicillin), possible surgical drainage or excision of infected tissue |
| Prognosis | Good with prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment; can be serious or life-threatening if untreated or misdiagnosed |
| Risk Factors | Poor dental hygiene, dental procedures, trauma to the face or neck, certain medical conditions (e.g., diabetes, alcoholism), iud use (pelvic actinomycosis) |
| Relevant Websites | Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) - For general health information, please click on the link |
The most common manifestation is cervicofacial actinomycosis, often presenting as a lumpy jaw. This form frequently arises after oral surgery or due to poor dental hygiene. In other cases, this may not be accompanied by pain. However, pain may develop along with the inflammation of soft tissues. The thoracic and abdominal forms are also frequent, and pelvic actinomycosis is possible in women. In the chest, it might mimic lung cancer or an anaerobic pulmonary abscess. In the abdominal area, the infection can resemble other serious conditions. Pelvic actinomycosis infections are most often associated with IUD use, but a unique presentation can be observed even in its absence.
Diagnosis hinges on a combination of factors. Doctors will consider your medical history, physical examination findings, and the presence of telltale signs such as abscesses, scar tissue, and fistulas. Imaging studies, such as CT scans or MRIs, can help visualize the extent of the infection. Crucially, laboratory identification is essential. Doctors will obtain samples of sputum, pus, or tissue and send them to the lab to check for various species of Actinomyces, such as Actinomyces israelii. This often involves inserting a needle through the skin to take a sample from an abscess or infected tissue.
The causal agent Actinomyces bovis typically found in the soil, the oral cavity of healthy animals, pasture, and farm premises, also plays a role in this. The organism enters circulation through mechanical wounds in the oral cavity. Proper wound management and clinical signs are key to diagnosis. The disease can be cured with proper treatment and management.
Treatment relies heavily on prolonged antibiotic therapy. Penicillin is the drug of choice, as Actinomyces is exquisitely sensitive to it. However, treatment duration is typically extended, often lasting for several months to ensure complete eradication of the bacteria and prevent relapse. In some cases, surgical intervention is necessary to drain abscesses or remove infected tissue. Prompt diagnosis and treatment significantly improve the prognosis, but delayed or incorrect diagnosis can lead to serious complications. This is why it's essential to consult with a healthcare professional if you experience any persistent or unusual symptoms, particularly if you have undergone dental work or experienced trauma to the face or neck.
Actinomycosis is an uncommon but significant subacute or chronic infection caused by anaerobic or microaerophilic bacteria, mainly within the Actinomyces genus. The bacteria often gains entry into the body via microfissures. The infection can affect various organs and tissues, leading to draining sinuses, abscess formation, and fibrosis. The disease is also a rare but serious bacterial infection that can affect various parts of the body. This article will walk you through the symptoms, types, causes, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of actinomycosis.
The bacterium's normal location in the nose and throat also means that actinomycosis most commonly affects the face and neck. The marked constitutional symptoms are a late feature that should suggest disseminated disease. It will often mimic lung cancer or anaerobic pulmonary abscess.