Missed Via Inka? Plus Inca History & Search Tips!
In the vast tapestry of history, what civilizations have left an indelible mark on the world, shaping cultures, and influencing the course of human events? The Inca civilization, a formidable empire that flourished in the Andes Mountains, stands out as a testament to human ingenuity, organizational prowess, and architectural brilliance, leaving a legacy that continues to captivate and inspire.
The quest to understand the Inca civilization begins with recognizing its remarkable geographical context. The Inca Empire, also known as Tawantinsuyu, meaning "the four parts together" in Quechua, spanned a vast territory along the Pacific coast and the Andean highlands of South America. Its reach extended from the northern border of modern-day Ecuador to the Maule River in central Chile. The empire's heartland, the Andes, presented unique challenges, including rugged terrain, high altitudes, and diverse climates. Despite these hurdles, the Incas not only survived but thrived, building an empire that boasted sophisticated infrastructure, advanced agricultural techniques, and a complex social structure.
The Incas did not leave a written language, but they meticulously recorded their history and administrative information using a system of knotted strings known as quipu. While the exact interpretation of quipu remains a subject of ongoing research, it is believed that these intricate devices were used to keep track of census data, agricultural yields, and even historical events. The Incas also kept lists of their kings (Sapa Inca), a practice that allows us to know such names as Pachacuti Inca Yupanqui, a pivotal ruler during whose reign (c. 1438-1471) the empire expanded significantly.
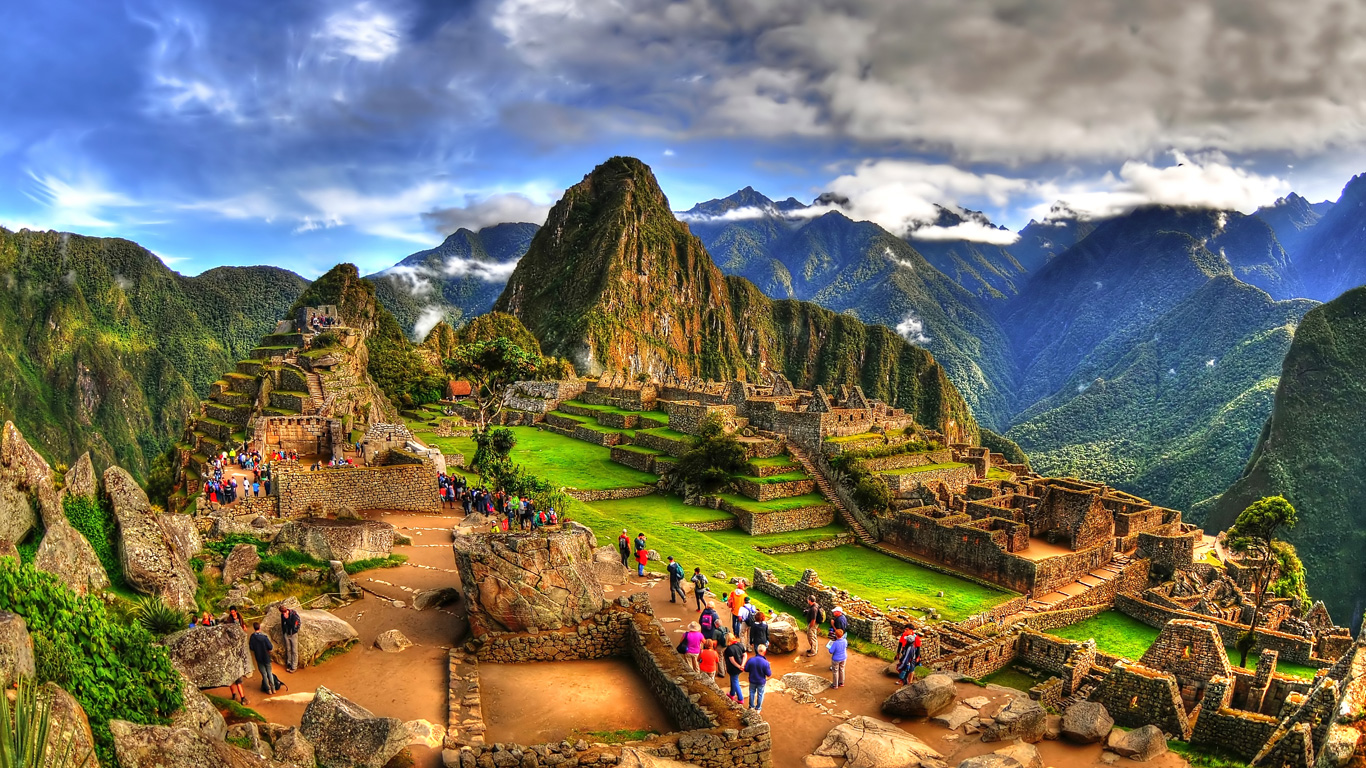
The descendants of the Incas still live today, primarily in and around the Andes, forming the largest ethnic group in Peru. Their enduring presence is a vibrant reminder of the Inca legacy and the resilience of their culture. The Quechua language, once the lingua franca of the Inca Empire, is still widely spoken in the region, further cementing the connection between the past and the present. The architectural marvels of the Incas, such as Machu Picchu, continue to draw visitors from around the world, offering a glimpse into the ingenuity and artistic achievements of this ancient civilization. It's a testament to the incas architectural and constructional expertise.
The Inca Empire's sophisticated administrative system was a key factor in its success. The empire was divided into four regions, each governed by a governor appointed by the Sapa Inca. A vast network of roads, known as the Inca Road system or Qhapaq an, connected these regions, facilitating communication, trade, and the movement of armies. The Inca Road system was an engineering marvel, built across challenging terrain, including mountains and canyons. This intricate system of roads, bridges, and tunnels allowed the Incas to maintain control over their vast empire and ensure efficient resource management. Furthermore, the Incas implemented a system of labor called mit'a, where communities were required to contribute a portion of their labor to public works projects, such as road construction and temple building.
In terms of agriculture, the Incas were highly innovative. They adapted to the challenging Andean environment by developing techniques like terrace farming, which allowed them to cultivate crops on steep slopes. They also mastered irrigation, constructing complex systems to channel water to their fields. Their main crops included maize (corn), potatoes, quinoa, and various fruits and vegetables. The ability to produce food in such a harsh environment was essential for sustaining their large population and supporting their complex society.
The social structure of the Inca Empire was hierarchical, with the Sapa Inca, the divine ruler, at the apex. The nobility, consisting of the Sapa Inca's family and high-ranking officials, held positions of power and privilege. Below the nobility were the commoners, who made up the majority of the population and were responsible for agricultural production, labor, and military service. The Incas also had a complex system of social organization based on the ayllu, a community-based unit that shared land and resources. Each ayllu was responsible for providing for its members and contributing to the empire's economy.
The Inca civilization's art and architecture were also remarkable. Their architecture is characterized by precision stonework, with massive blocks of stone fitted together without mortar. Machu Picchu, a mountaintop citadel, is perhaps the most iconic example of Inca architecture. The Incas also created intricate textiles, pottery, and metalwork. Their artistic expressions reflected their beliefs, their social structure, and their connection to the natural world.
The Inca civilization's downfall came with the arrival of the Spanish conquistadors in the 16th century. The Spanish, led by Francisco Pizarro, exploited internal divisions within the Inca Empire and introduced diseases that decimated the Inca population. The Spanish conquest resulted in the collapse of the Inca Empire and the imposition of Spanish rule over the region. The conditions of the Inca nobility were not accepted by the Spanish encomenderos, who believed that this social class could lead uprisings and revolutions, however, for a century, the nobility was recognized and accepted.
Despite the conquest, the Inca legacy endures. Their architectural marvels, agricultural techniques, and social systems continue to inspire and influence. The descendants of the Incas preserve their cultural traditions, language, and identity, ensuring that the memory of this remarkable civilization lives on. The impact of the Incas can still be felt throughout the Andes and beyond. Their contributions to the world include the development of sophisticated agricultural methods, advanced engineering skills, and a unique social and political structure. The study of the Incas continues to shed light on the complexity of human societies and the potential for innovation, organization, and adaptation in the face of challenging environments.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Name | Inca Civilization (Tawantinsuyu) |
| Geographic Location | Pacific coast and Andean highlands of South America, from modern-day Ecuador to central Chile. |
| Period | Flourished from the 15th to the 16th centuries. |
| Key Rulers | Pachacuti Inca Yupanqui, Topa Inca Yupanqui, Huayna Capac |
| Language | Quechua |
| Notable Achievements | Sophisticated road system (Qhapaq an), terrace farming, intricate stonework architecture (Machu Picchu), quipu system for record-keeping, advanced social organization. |
| Social Structure | Hierarchical: Sapa Inca (ruler), nobility, commoners, ayllu (community units). |
| Economy | Based on agriculture, trade, and tribute. |
| Decline | Conquest by the Spanish conquistadors led by Francisco Pizarro in the 16th century. |
| Legacy | Influence on Andean cultures, architectural marvels, agricultural techniques, and cultural traditions that continue to be practiced by descendants today. |
| Modern Relevance | Inca descendants are still a large ethnic group in Peru. |
| Reference | Britannica - Inca Civilization |
In the realm of news and information, we often encounter difficulties. For example, when seeking information, a search query may return, "We did not find results for: What happened to via inka," indicating a lack of readily available, specific information. The search engines might also display "Check spelling or type a new query." when a user's search term has a potential error, or that the search system is unable to immediately provide a match to the exact term entered. The information availability is not perfect, which is something common in the digital world. This demonstrates the constant need for more precise searches or for the refinement of the information-seeking process, which can also be applied to the study of Inca civilization.
The vastness of the Inca Empire and its complex social structure are difficult to comprehend fully, and the lack of a written language further complicates historical research. Despite this, many details about the Inca's customs, social structure, and achievements have been well preserved. The Inca civilization's story is a great example of adaptation, ingenuity, and resilience. Their ability to create an empire in such a challenging environment continues to resonate today.
In the modern age, we have many resources available, but finding precise information might sometimes still be difficult. The availability of the information may vary, so it's good to refine your search terms and check that the spelling is right. These challenges also remind us of the challenges faced by the Incas, who had to invent new solutions using the resources that they had available. They created a society that was very successful and adapted very well to the environment they lived in. The Incas left a significant mark on the world, proving that the human spirit can thrive even in the face of great difficulties. Their success should continue to inspire us to investigate and to be curious.
From an entirely different perspective, you may come across issues related to online transactions or scams. If you encountered this message: "This literally happened to me today and I wasn't able to complete the task so my money is on hold," or "I've started researching about this scam and this exact thing happened to me", it is very important to proceed with caution. You can find yourself in a complex situation, and the steps you take may have real consequences. Researching the specifics, finding the relevant information, and getting help are often the most important ways of dealing with this kind of problem. There are many resources and support networks, so being informed and getting help from the proper channels is often the best path to take. The Incas achievements were the outcome of a society that was well-organized and managed, and in that case, knowledge of what happened or the support of the right resources are key in the management of different situations.